All Technologies Used
Motivation
The client needed a modern banking platform for SMEs because their legacy monolithic system was inflexible, caused performance bottlenecks, and lacked tools for efficient payment processing, account management, and reporting. The goal was to deliver a scalable, resilient, and high-performance system that could handle increasing transaction volumes, improve operational efficiency, and ensure uninterrupted service during peak financial periods.
Main Challenges
The legacy monolithic architecture limited flexibility and scalability. Azati led the migration to a microservices-based structure, significantly enhancing modularity and performance.
The system had to maintain high availability and reliability, especially during peak times such as tax periods and holidays. Load testing and incident response processes were established to ensure readiness.
The system scaled from processing 10,000 payments per month to over 1 million per day. Performance optimization and architecture redesign were key to supporting this growth.
Our Approach
Want a similar solution?
Just tell us about your project and we'll get back to you with a free consultation.
Schedule a callSolution
Multichannel Payment Support
- Payment creation across online, mobile, and batch channels
- Support for recurring and one-time payments
- Integration with bank clearing systems and APIs
- Real-time status tracking of all payment operations
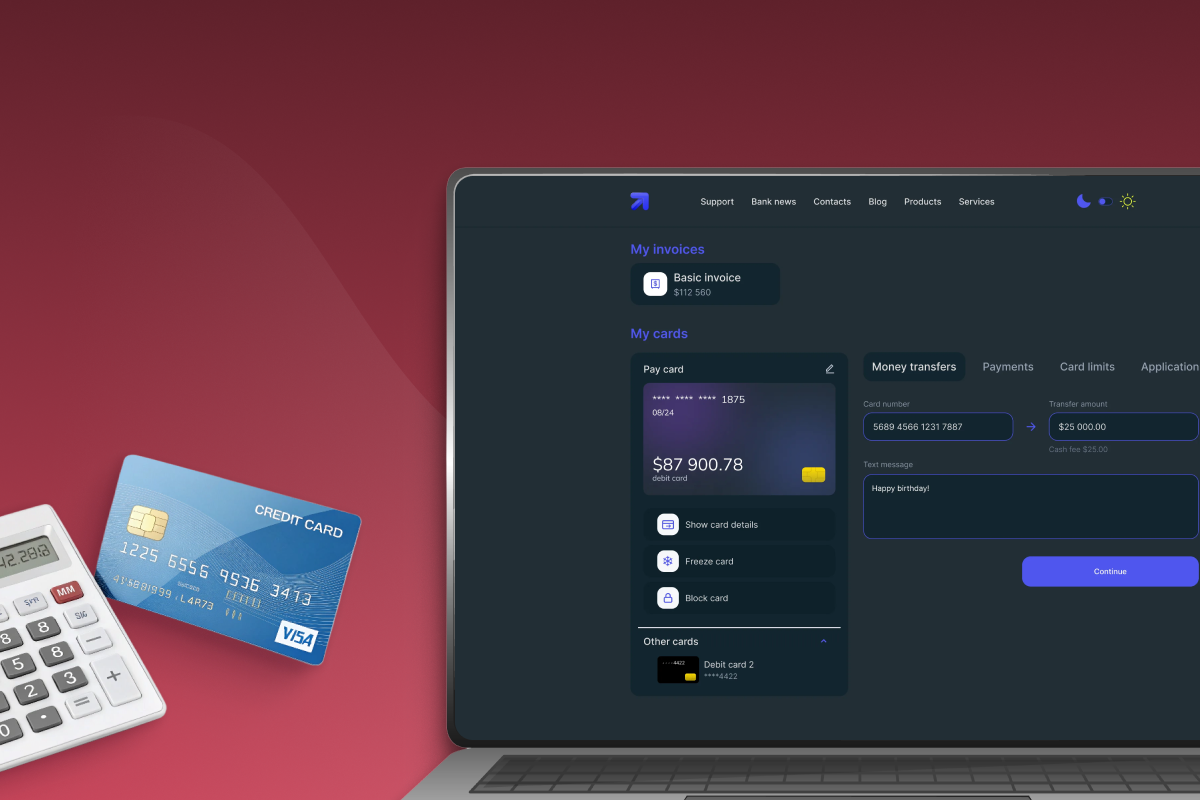
Account and Card Information
- Real-time account balance updates
- View and manage multiple business accounts
- Detailed card and transaction information
- Search and filter historical transactions for auditing
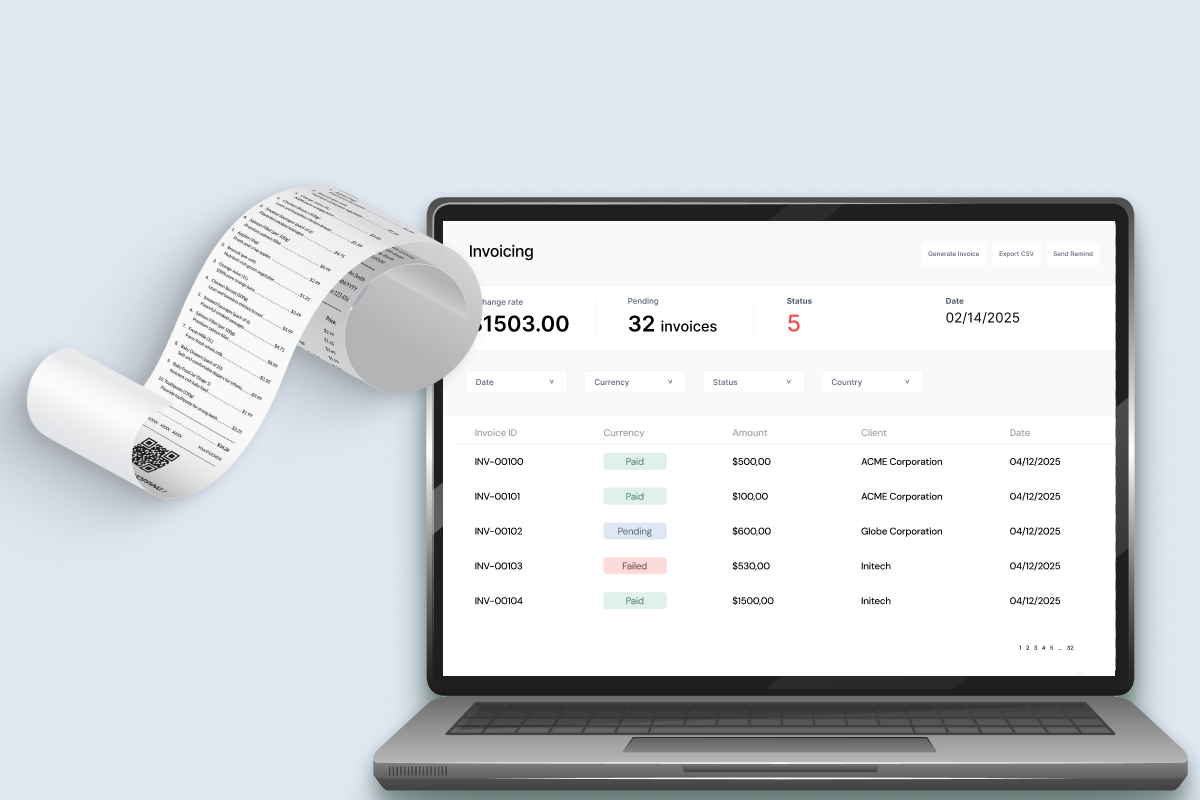
Dynamic Reporting
- Customizable reports for payments, accounts, and balances
- Export in PDF, Excel, or CSV formats
- Automated scheduled report generation
- Data aggregation for compliance and auditing purposes
Microservices Architecture
- Independent deployment of individual services
- Fault isolation and improved system reliability
- Scalable architecture to handle increasing loads
- Clear separation of business logic for maintenance
High-Performance Messaging
- Asynchronous messaging between services
- Reliable transaction processing
- Real-time event streaming for financial updates
- Integration with multiple backend systems and services
Production Monitoring and Support
- Continuous monitoring of system health and transactions
- Proactive incident detection and resolution
- Load testing before high-traffic periods
- Alerting and reporting for operational oversight
Business Value
Successful Microservice Migration: Transitioned from monolithic to microservice architecture, increasing system scalability and deployment efficiency.
Enhanced Stability and Uptime: Improved system resilience, reduced production incidents, and ensured uninterrupted financial services.
High-Load Readiness: Prepared the system for peak seasons, enabling smooth operation during high-traffic periods like tax payouts.
Accelerated Development Cycle: Streamlined development and testing workflows, reducing release times and improving delivery speed.
Massive Throughput Growth: Scaled the system from 10,000 monthly payments to over 1 million daily, showcasing robust architectural evolution.
Technological Modernization: Migrated the system to Java 17 and replaced foreign software with domestic alternatives, aligning with import substitution initiatives.